Clickable Prototype
Get feedback on your product by creating a Clickable Prototype! Read how to create an efficient one.
What Is a Clickable Prototype?
A Clickable Prototype shows a visual representation of the user interface of a website or software application. Unlike static wireframes or mockups, it can show several states of the application - for example, a drop-down menu, or initially hidden additional information or fields may appear. A Clickable Prototype offers an interactive experience very similar to a finalized application.
Prototypes are often made in the cheapest way and usually at a lower level of detail than a final product.
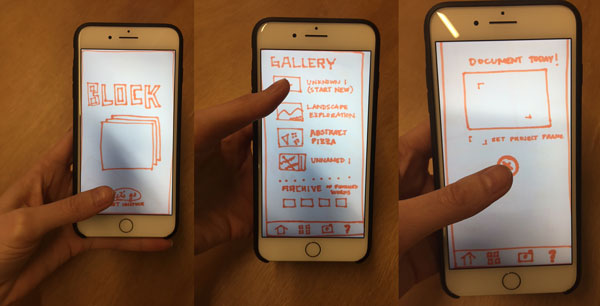 Source: Create and test your clickable prototype
Source: Create and test your clickable prototype
Why You Might Want a Clickable Prototype
A Clickable Prototype is used as a presentation of the future product to gather more accurate feedback (typically via UX tests) from:
- Product owners/decision makers They choose what is in and out of scope and what is part of MVP. Clickable Prototypes help to generate support, gain agreement or even investment for the project.
- Developers It helps them to better understand the product. A prototype may reduce misunderstanding between developers and product owners or UX experts.
- End users It lets them realize and confirm what they want. By using prototyping as an agile tool it is possible to test theories and ideas (for example, design or layout of the website). Prototypes help prevent drastic late changes or even rejection of the finalized product.
Software development which using prototyping can be faster and more cost-effective than programming, minimizing wasted effort on unwanted functionality.
Problems the Clickable Prototype Solves
- Demotivated team
- Increased cost
- Unsuccessful product
- Unhappy clients
- Disconnect Between Business and IT
- Poor code quality
- Bad Product-Market Fit
How to Implement the Clickable Prototype
It is recommended to start with a simple wireframe (pen + paper). Your head thinks only about the prototype and not about the tool. If your paper Clickable Prototype is not sufficient for the purpose, continue with advanced prototyping.
Keep particular versions of the prototype, because you might want to come back to an initial idea during the project. It is possible to reuse some components among projects (for example, a menu bar across a corporate internet banking system).
There are a lot of prototyping tools on the market, such as Axure, Sketch, Balsamiq, Proto.io or Justinmind.
It is possible to create a great prototype with PowerPoint or Keynote. A prototyper is usually a UX designer and does not necessarily have developer skills.
Common Pitfalls of Clickable Prototype
- Slowdown A Clickable Prototype usually clarifies communication between decision makers and the rest of the team. Sometimes it can conversely cause a slowdown of development, for example UX specialist/prototyper is on the other end of the globe than product owner and developer. Communication can be in this case very difficult.
- Unnecessary It follows the point above: sometimes programming possible scenarios can be cheaper and faster than prototyping, and a paper or a blackboard wireframe might be sufficient. Consider whether it is necessary.
- Too much detail The level of detail of the Clickable Prototypes should depend on the type of project. For example, a prototype for usability testing might be closer to the reality than for presentation on management board.
- Stakeholders are confused Stakeholders sometimes think that the Prototype is the final product. Ensure that they have enough information about what the Prototypes are for.
Resources for the Clickable Prototype
- KFG Blog: Why Product Clickable Prototype Is Different and What Tools to Use to Make One
- Experience UX: What Is Website Prototype?
- Pidoco: Clickable Wireframe
Was the article helpful?
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Prokop Simek
CEO
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
Fail Fast
Fail Fast is a method used during a recurrent approach to determine whether an idea has a value for the client or solution. An important goal is to minimize losses when testing reveals something is not working and quickly try something else.
Read moreDesign Sprint
A Design Sprint is a framework that reduces the risks associated with product development. It is an intense process done by a small team in just 3 - 5 days.
Read moreWireframing
Wireframing is a visual tool to create a scheme of the user interface (UI) without focusing on graphic design. It helps to get a better picture of the elements that will be programmed.
Read morePenetration Testing
Penetration Tests are performed to identify network security weaknesses. It is a "friendly cyberattack" for spotting flaws and potential vulnerabilities.
Read moreMVP
The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a scope of a product with the smallest possible functionality which is able to provide meaningful feedback from users.
Read moreALL ARTICLES
Contribution
We are happy you want to contribute to DXKB. Please choose your preferred way