Design Thinking
Design thinking puts a user at the center of the product design. It means that users' needs and wants are prioritized first by taking an ergonomic and iterative approach during designing. This article will learn how design thinking is used to create better designs that provide satisfying solutions to the users.
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking involves developing design concepts that are user-centric by applying cognitive, strategic, and practical processes. Design thinking encompasses an ergonomic approach by integrating psychological and physiological principles into the design process. Understanding what users want or need and how a particular design will affect their lives is crucial.
The design process has evolved from conservative mode and progressed to an open-minded human-centric approach that eliminates self-imparted dictatorial views on how users should interact with a particular product. Design thinking relies on available variables that define and describe users' needs and wants and then translate them into empirical evidence for designing and prototyping the final solution.
 Source: Medium: How to use design thinking in the UX design process
Source: Medium: How to use design thinking in the UX design process
Why You Might Want Design Thinking
The world is swiftly moving away from one-person imparted views to an open-minded direction that values the total inclusivity of every category of users. Design Thinking helps to take inclusivity to a whole new level during the process of designing any product. The designer understands how to provide a satisfying and non-discriminatory solution to all users through empirical observation.
Design thinking is also treated as the new normal of the modern designing approach. Most companies are rapidly embracing it while moving away from old-fashioned conservative methods that dictate what users need or want. Popular and highly profitable companies like Apple, Microsoft, Toyota, Nike, and many others have incorporated design thinking into their product design and development strategies.
These days, your potential customers want to feel like they're part of the product design process, which means putting and understanding their needs first. It would be illogical to create a product with a rigid design that doesn't fit users' expectations.
Problems Design Thinking Solves
Design thinking offers a whole package of advantages to the designer and the user by eliminating the prevailing problems like;
- Diversity Gap. Companies prioritize diversity and inclusiveness when designing products for customers these days. Using design thinking helps them identify different behavioural patterns of various groups of users to be reconciled and fitted into the "design for all" perspective. Design thinking helps them eliminate diversity biases resulting from self-preconceived notions when designing a product.
- Meaningless innovation. The best ideas always present the best design. And the best design can make a good product or solution for the users. Design Thinking is the core innovation, as it relies on gathering critical variables that define what users need or want. And the designer depends on the gathered data to produce the best design, offering the best solution for the users.
- Toxic teamwork culture. When working as a group, design thinking encourages collaboration and brainstorming ideas.
- Misallocation of resources. Designing a product without considering what users want can lead to total misallocation of resources, causing the designer financial severe losses. Design thinking presents an organized way of doing things because it helps the designer know what needs to be done.
How to Implement Design Thinking
Design thinking involves overlapping stages rather than sequential steps because it considers that designing is iterative and often integrates with continuous refining of ideas and developing new directions. The methodological implementation of design thinking is fulfilled through a 5-stage framework.
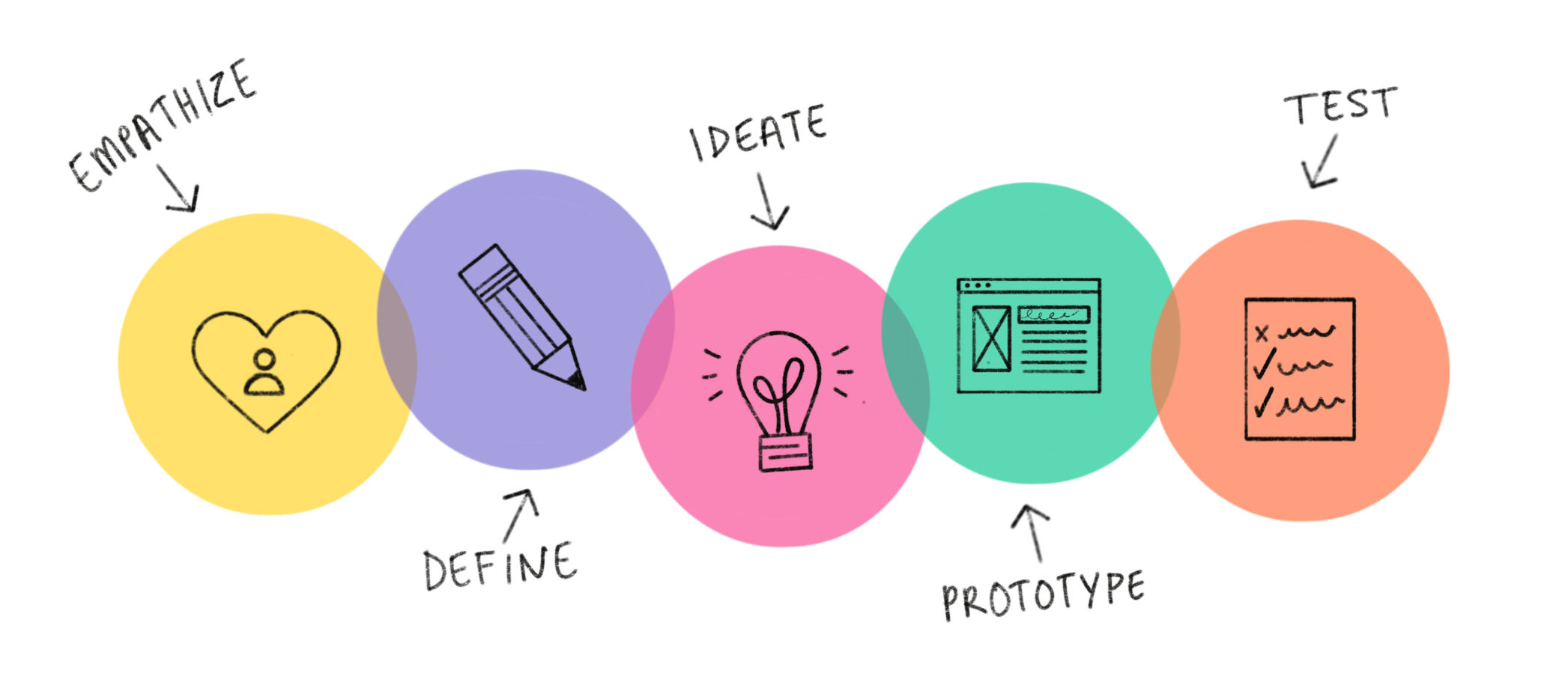
Understanding the 5-Stage Framework of Design Thinking
The five stages involved include:
-
Empathy: In this phase, the designer examines and identifies key variables that define strict ergonomic requirements that cannot ignore during the design process. The human-centric approach of designing assesses how a particular design will affect the user psychologically and physiologically and takes empathy to appreciate this fact. An empathetically empirical method is a good way of observing and understanding how users can interact with the product. It takes open-mindedness and applies bias-neutral notions to avoid imparting self-defined preconceived views on what users need or want. It democratizes the process of designing because it puts the users' psychological and physiological satisfaction first and doesn't rigidly dictate a one-person view of them.
-
Define: The final endpoint of any design is to offer a suitable and satisfying solution to the user. However, we can't devise those solutions without defining the problem. In this stage, a designer uses the collected data from the empathy stage and pieces it up to determine the problem that needs to be solved. The empirical data collected gives a designer an understanding of the problem, enabling him to formulate the best strategy for the user. For instance, a computer mouse designer may collect data regarding the complexity of using the current mouse design. Does he understand why the contemporary design is complicated for users to use? How complicated is it? What is the perspective from users, and what do they want? Does the current design drastically affect users psychologically and physiologically? The answers obtained after asking these kinds of questions help the designer define the problem and crack the best solution.
-
Ideate: Congratulations, you've successfully defined the problem in the defined stage! It is now time to brainstorm ideas that could translate into an actual solid solution. A collaborative approach is one of the best ways to brainstorm good ideas. If you're in a group, you work with your team members to develop a powerful concept that can offer the solution needed by the user.
-
Prototype: A Chinese Philosopher once said, "A journey of 1000 miles begins with one step". An idea is as good as nothing else if translated into an actionable solution. Any design idea has to be prototyped to streamline a solution needed by the user. A prototype helps you test out what the users think of the design, and the feedback you collect from them allows you to finetune the strategy, thus delivering the best solution.
-
Testing: The testing stages go hand in hand with the prototype stage. The truth is the prototype doesn't represent the final product; however, it is used to turn an idea into action that represents a solution. When a prototype is finalized, the designer can invite users to test it and evaluate how they interact. The design thinking process embodies an iterative philosophy that eliminates a linear approach in the design process. When the users' feedback doesn't favor the current design, the designer can iteratively go back and make some changes to suit the best solution needed ideally.
Common Pitfalls of Design Thinking
- Collecting critical data about potential users is costly. A designer must first understand the user behaviours before creating the appropriate design that can provide the solution they need. It often needs resources to research potential users.
- It creates friction when aligning users' needs and the designers. Both the users and the designer may have different perspectives about what is needed, resulting in a paradoxical situation.
- Understanding and satisfying all users’ psychological and physiological needs is not easy. Design thinking emphasizes ergonomics in the design process, but this cannot be easy.
- It is tiresome to keep iterating the design. Design thinking forbids a linear approach during the design process. It makes the whole process tiring as the designer has to keep repeating or updating the design in response to the users' feedback received.
Resources for Design Thinking
- Interactive Design Foundation: What is Design Thinking and why is it so popular
- Harvard Business Review: Why Design Think Works
- IDEO: Design Thinking Defined
- We work: What is Designing and why is it important
Was the article helpful?
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Prokop Simek
CEO
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
MVP
The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a scope of a product with the smallest possible functionality which is able to provide meaningful feedback from users.
Read moreDesign Sprint
A Design Sprint is a framework that reduces the risks associated with product development. It is an intense process done by a small team in just 3 - 5 days.
Read moreFail Fast
Fail Fast is a method used during a recurrent approach to determine whether an idea has a value for the client or solution. An important goal is to minimize losses when testing reveals something is not working and quickly try something else.
Read moreLean Canvas
A Lean Canvas is a 1-page chart with 9 basic building blocks. It helps to identify problems and solutions for your product.
Read moreTest Cards
Test cards help you to test and validate your business ideas by defining how you will test them, what you will measure, and what success looks like.
Read moreALL ARTICLES
Contribution
We are happy you want to contribute to DXKB. Please choose your preferred way