Lean Canvas
Print this chart, fill the 9 fields, and you are ready to build a successful product.
What Is a Lean Canvas
Lean Canvas is a very useful visual planning method. It is a big chart with 9 fields describing the key assumptions of your business model. It is used for:
- Creating a new product or for developing an existing one.
- It helps you identify the uncertainties and risks.
- It can be used for the whole product and also for each product feature.
Lean Canvas was created by Ash Maurya as a development of the Business Model Canvas.
The whole team has to participate in creating the Lean Canvas model. All the 9 fields in the scheme have to be filled and it should not take longer than 20 minutes. It is recommended to fill the chart in the following order, and then read it from left to right:
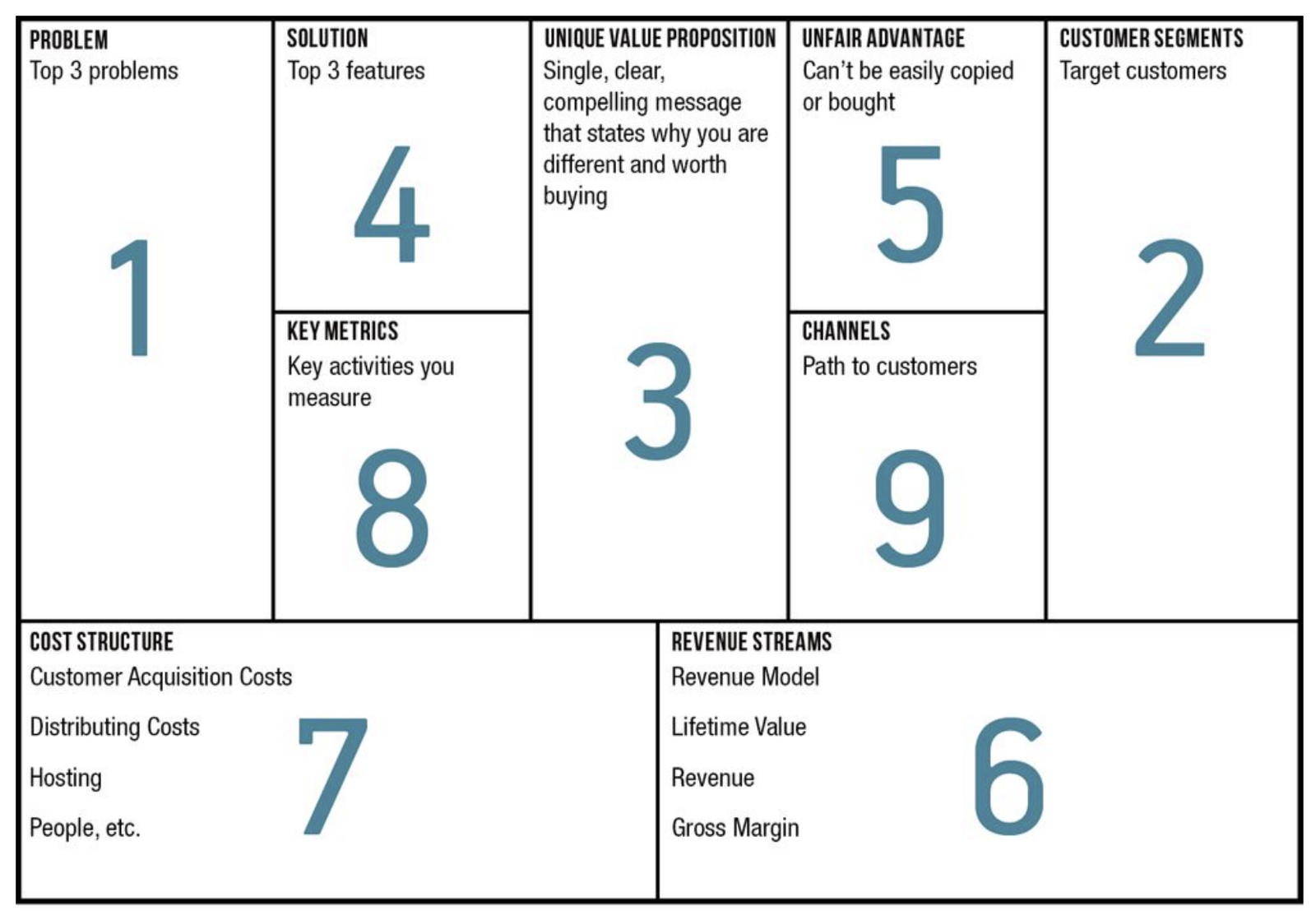 Source: Leanstack: What Is The Right Fill Order For A Lean Canvas?
Source: Leanstack: What Is The Right Fill Order For A Lean Canvas?
- Problem
- Customer segment
- Unique value proposition
- Solution
- Unfair advantage
- Revenue streams
- Cost structure
- Key metrics
- Channels
To get the correct output, the scheme requires data from the following teams:
- Business Team
- Analytic Team
- Compliance Team (for defining the customers' segment)
- Technical Leaders
- Product Management
Why You Might Want the Lean Canvas
Lean Canvas quickly addresses the important question: is the business project worth creating?
A simple visual chart helps with communicating the offer to customers. It is clear, easy to share and it can be updated as frequently as needed. It also helps with creating the elevator pitch or MVP (minimum viable product).
Lean Canvas is also an easy tool for the team to help them understand the business product.
Problems the Lean Canvas Solves
- Demotivated team
- Increased cost
- Bad product-market fit
- Meaningless work
- "Not my problem" mentality
- Unhappy client
- Toxic team culture
- Disconnection with business
How to Implement the Lean Canvas
The chart can be created:
- As the very first step when designing a new product
- During strategic planning sessions
- For the whole product or business plan
- For each product feature
- With the team
- With the business partners
All you have to do is to get the right people from your company or/and your business partners together and fill the chart. You can use a Lean Canvas generator, such as Canvanizer or Leanstack.
Common Pitfalls of the Lean Canvas
- Make sure to fill the chart with an open mind. A common mistake is to have the conclusions already in mind and to adjust the chart to reach them.
- Avoid refilling the chart if the conclusions are not as positive as expected.
- Lean Canvas is commonly mistaken to be a tool only for startups. The chart can be used by a company of any size and any business approach. It was proven to be useful for documenting the product at any stage of development.
Resources for the Lean Canvas
- Leanstack: The Lean Canvas
- Medium: Lean Canvas is the New Business Plan
- Leanstack: Why Lean Canvas vs Business Model Canvas?
- Leanstack: Why and How to Model a Non-profit on the Lean Canvas
- Leanstack: A Lean Canvas is NOT Enough to Replace a Business Plan
- Youtube: Lean Canvas Example
Was the article helpful?
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Prokop Simek
CEO
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
Design Sprint
A Design Sprint is a framework that reduces the risks associated with product development. It is an intense process done by a small team in just 3 - 5 days.
Read moreMVP
The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a scope of a product with the smallest possible functionality which is able to provide meaningful feedback from users.
Read moreDesign Thinking
Design thinking puts a user at the center of the product design. It means that users' needs and wants are prioritized first by taking an ergonomic and iterative approach during designing.
Read moreValue Proposition
A Value Proposition Canvas is a model that helps to ensure that a product covers customer’s requirements. It defines the customer segment and the value proposition.
Read moreFail Fast
Fail Fast is a method used during a recurrent approach to determine whether an idea has a value for the client or solution. An important goal is to minimize losses when testing reveals something is not working and quickly try something else.
Read moreALL ARTICLES
Contribution
We are happy you want to contribute to DXKB. Please choose your preferred way