Automated Deployment
If there is one golden rule in programming, it should be to automate as much as possible. Automated Deployment ensures that the path your code takes from development through to production does not break its functionality. Read more to learn how to make Automated Deployment a regular part of your Continuous Deployment.
What Is an Automated Deployment
Automated Deployment is a practice that allows you to ship code fully or semi-automatically across several stages of the development process - from initial development right through to production. It contributes to more efficient and reliable deployments.
How do you know that the path your code takes from development to production does not break its functionality? To ensure functionality you should automate as much as possible. Automation requires a deployment pipeline, which is the process of taking code from your version control environment (for example, git) and making it available to users of your application.
We can classify Automated Deployment approaches into different categories, according to the level of automation coverage across environments:
- Continuous Integration Continuous Integration is the practice of daily integrating code changes. Everything that has been developed integrates daily. Each integration is then automatically verified and tested to detect possible errors. For more information, see Continuous integration.
- Continuous Delivery Continuous Delivery is the practice of keeping the code ready to deploy at any given time. Continuous Delivery is an extension of the continuous integration to automate release to the staging environment. Continuous Delivery ensures a a production-ready version of your build at any time. This is often required by financial institutions and other customers who require little or no "down time".
- Continuous Deployment Continuous Deployment is the practice of fully automating the entire process of the deployment pipeline. Every change in the source code is deployed to production automatically and without explicit approval from a developer. This is the quickest method of deployment, however errors can cause issues and possible downtime.
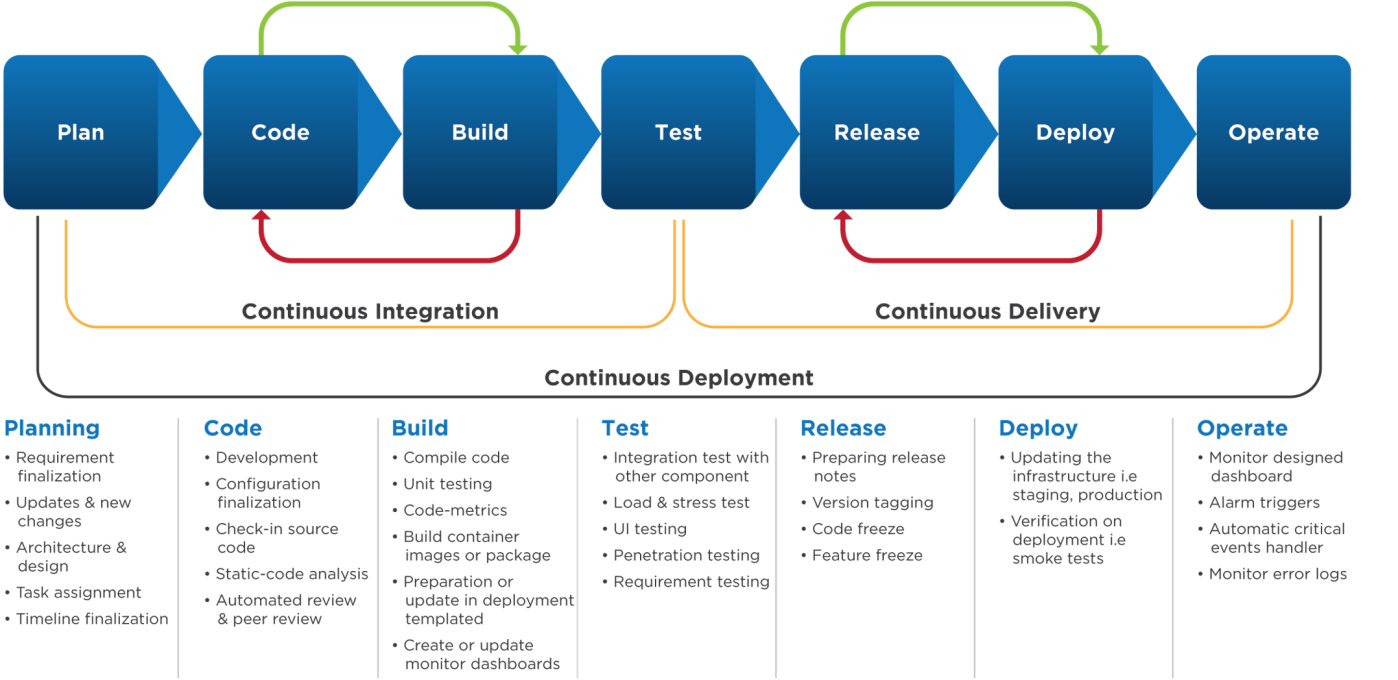 Source: Secure and Scalable CI/CD Pipeline With AWS
Source: Secure and Scalable CI/CD Pipeline With AWS
Why You Might Want the Deployment to Be Automated
Automated Deployment helps your team with:
- Reduced possibility of errors Manual deployment is error-prone. Any process involving human input introduces the possibility of errors. Assignment to repetitve manual deployment tasks can harm employee morale.
- Saving time Manual deployment is time-consuming. The job is often assigned to testers and developers in a development team who can otherwise spend their time working on improving the application.
- Consistency and repeatability Once configured, the process is the same every time you initiate release. It contributes to more frequent and stable releases. This consistency greatly assists in diagnosis of errors as it reduces the possible variables.
Issues the Automated Deployment Solves
- Increased cost
- Poor Code Quality
- Meaningless Work
- Developers vs. Operations wars
- No runtime version management
- Long Feedback Loops
How to Implement Automated Deployment
Follow these steps to set up a basic deployment pipeline:
- Set up a Continuous Integration server
- Set up a few test suites
- Set up a separate build for each test suit and link the builds like dominos, so that each is triggered by the one before it. This way you see very quickly if there is some problem - the problematic code change stops at the first test that recognizes it and does not go any further.
- Add a deployment step
- On your Continuous Integration server, set a build that runs your script to deploy your application to a testing or staging environment. Ensure that it runs only when all the tests pass.
Common Pitfalls of the Automated Deployment
- Exaggerated reliance on the Automated Deployment It is always good to have an alternative strategy to avoid being stuck when your Automated Deployment configuration is broken.
- The project is too small Implementing Automated Deployment can be time-consuming. Ensure that you do not spend more time implementing it than actually developing the product.
- Rigid pipeline design Rigid pipeline prevents the team from optimizing their processes. Pipeline should be structured, flexible, and able to incorporate sudden changes.
- Long and slow deployment pipelines There are too many steps between code commit and deployment. Ensure that every step is necessary.
Resources for the Automated Deployment
- Electric Cloud: Deployment Automation
- Atlassian: Practical Continuous Deployment
- TechBeacon: Running the gauntlet: Setting up your first deployment pipeline
- Freecodecamp: Learn how to automate deployment on GitHub pages with Travis CI
- FlavioCopes: Deploy Node.js application with Zeit Now
Was the article helpful?
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Prokop Simek
CEO
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration is a software development practice that makes developers integrate code changes into a shared repository routinely and frequently. Usually, each person integrates at least daily and that ensures them that their code changes do not break anything.
Read moreDevops
DevOps is a set of practices that brings development and operations teams together. The collaboration helps to release software much faster.
Read moreContinuous Delivery
Practicing Continuous Delivery means that you adopt practices to be ready to release product changes any time you want. Your product is always ready to deploy to production.
Read moreKanban
Kanban is a Lean method similar to Scrum. It is focused on managing a continuous delivery of products with avoiding the "bottleneck effect". It helps teams work together and more effectively.
Read moreRelease Management
Release management is the process of managing, planning, designing, scheduling, testing, controlling and deploying of a software build through different stages and environments; in preparation for software releases.
Read moreALL ARTICLES
Contribution
We are happy you want to contribute to DXKB. Please choose your preferred way