Devops
DevOps is a set of practices that brings development and operations teams together. Read how to make them collaborate and, therefore, deliver software much faster.
What Is a Devops
DevOps is a set of practices that combines the work of two teams: software development (Dev) and information technology operations (Ops). These two teams usually work separately, which is not always efficient. If they implement the DevOps strategy and start to collaborate, they can build, test and release software much faster and safer. DevOps is both technology and a culture change, it can be difficult to implement it. The teams have a DevOps Engineer to help them with this change and with the collaboration.
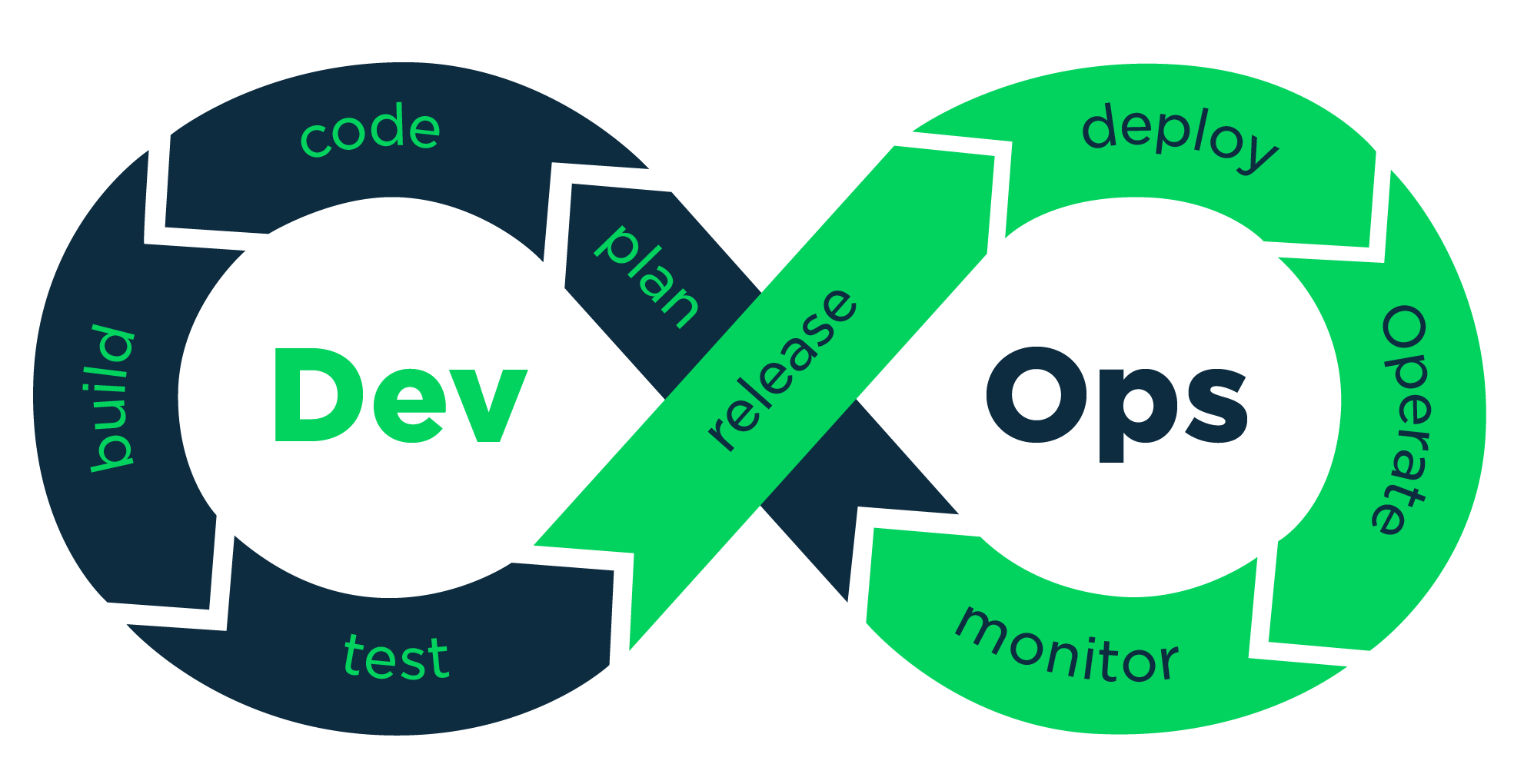 Source: Medium: DevOps is a culture, not a role!
Source: Medium: DevOps is a culture, not a role!
Who Is a DevOps Engineer
The DevOps Engineer can be originally from one of the teams. After the implementation of the DevOps strategy, they become part of the other team as well. The role needs someone with hard and soft skills to blur the barriers between the teams.
Skills the DevOps Engineer Needs:
- Soft Skills
- Especially communication skills - they have to be able to explain complex situations
- They need empathy to be able to talk to both teams
- They have to be good problem solvers
- Understanding of tools and technologies
- They have to understand what tools or programs the developers use
- Knowledge of coding
- At least a basic knowledge of coding is necessary
Flexibility The DevOps Engineer has to be time flexible. Sometimes problems in different fields rely on them. It is necessary to be able to cover it all.
Why You Might Want the DevOps
The DevOps builds culture and trust in your company. It helps with sharing responsibility and transparency, accelerating the feedback, managing unplanned work, and resolving issues among both teams. It makes the team members think beyond their own teams - their actions affect all the other teams involved. Sharing goals and progress banishes the ‘not my problem’ attitude. The teams that practice DevOps are more productive and release more frequently. The developers can see the results of their work.
Problems the DevOps Solves
- Increased cost
- Demotivated team
- "Not my problem" mentality
- Developer vs Operations wars
- Long feedback loops
- Increased cost
- Bad product-market fit
- Meaningless work
- Toxic team culture
- Disconnect Between Business and IT
How to Implement the DevOps
Culture To implement the DevOps, the company has to start with changing the culture of collaboration. Take small steps, invite members of the operation team to the meetings of the development team. Operation team can invite key developers to their meetings. That way everyone can keep up with other’s projects. Make sure that everyone understands the DevOps culture and that they communicate and talk regularly.
Automation Automation is another necessary step in implementing DevOps. It eliminates repetitive manual work and builds a system beneficial for both teams.
Lean Continuous improvement of a product is very important. A product is more valuable for a customer if it goes with constant maintenance. Even if it is not perfect at the beginning.
Measurement It is necessary to have some data to be able to continuously improve a product. It is important to ask testable questions. For example, how often the bugs appear? How many people use the product? All the data helps the team to make decisions and to share the information about a product with other teams (for example, marketing).
Sharing Sharing is crucial. If the teams share responsibilities, they share success as well. It is important for building trust and a good atmosphere at work.
Common Pitfalls of DevOps
- Developers do not identify themselves with DevOps practices. The culture change did not happen.
- Lack of support from management: the managers do not support the changes enough.
- No tooling or no automation
- Lack of dedicated resources: the company believes that everyone uses DevOps practices but in reality, they do not identify themselves with the DevOps.
- DevOps Engineers work only as one of the other developers and does not create the culture change. The operations team does not trust them and do not cooperate.
Resources for the DevOps
- Atlassian: DevOps
- The New Stack: Want Devops Automation? It’s People Before Pipelines
- Knowledge Hunt: DevOps & Automation- Advantages Of DevOps
- TechBeacon: Demystifying the DevOps role: 3 lessons for success
- Tech Republic: 10 critical skills that every DevOps engineer needs for success
Was the article helpful?
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Prokop Simek
CEO
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
Kanban
Kanban is a Lean method similar to Scrum. It is focused on managing a continuous delivery of products with avoiding the "bottleneck effect". It helps teams work together and more effectively.
Read moreContinuous Integration
Continuous Integration is a software development practice that makes developers integrate code changes into a shared repository routinely and frequently. Usually, each person integrates at least daily and that ensures them that their code changes do not break anything.
Read moreRelease Management
Release management is the process of managing, planning, designing, scheduling, testing, controlling and deploying of a software build through different stages and environments; in preparation for software releases.
Read moreContinuous Delivery
Practicing Continuous Delivery means that you adopt practices to be ready to release product changes any time you want. Your product is always ready to deploy to production.
Read moreAutomated Deployment
An Automated Deployment allows an application to be deployed across various stages of the development process. It minimizes the need for manual intervention.
Read moreALL ARTICLES
Contribution
We are happy you want to contribute to DXKB. Please choose your preferred way