UX Prototyping
A UX Prototype is a model of the product or service or process you're designing intended to give the design team better information to inform their decisions. It's usually used to test elements or principles but can be used to illustrate ideas. It should be much cheaper than the finished product so it can be modified or even thrown out without any problem.
It should not be seen as a final design candidate or MVP.
What is a UX Prototype
As mentioned above it's a model, a simplified version of a system meant to test or present specific aspects of it. It can be a sketch on a whiteboard that helps the design team walk through a complex process, it can be a set of web page mockups intended to test target audience reactions to graphic elements. It can include on and offline elements, even a full-scale model of a brick & mortar storefront. The form of the model depends on the information being sought, the abilities of the team to build it, and of course the budget available.
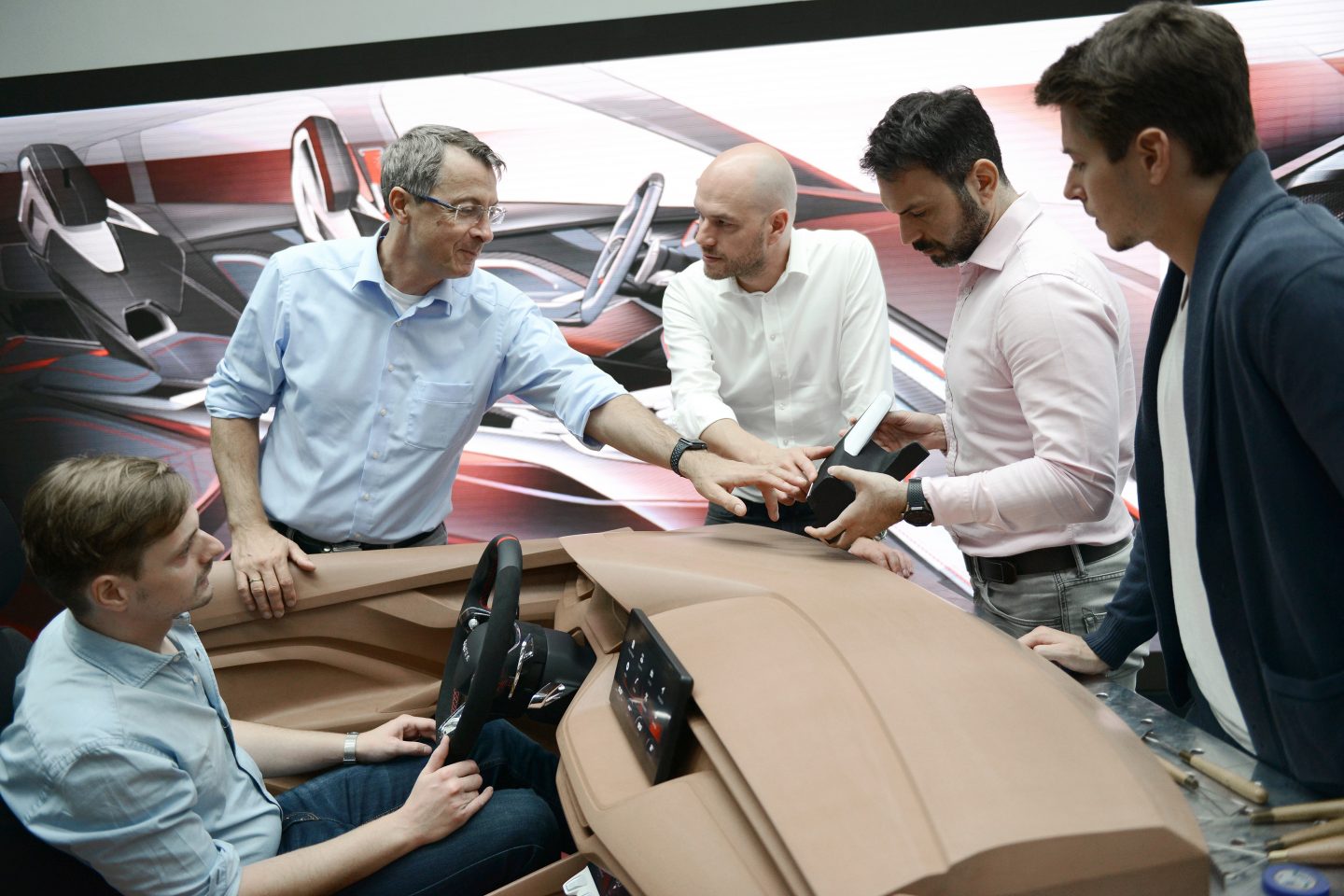 Source: Skoda Storyboard
Source: Skoda Storyboard
The types of prototypes really can be endless. In general, they should focus on getting specific information needed by the design team or to present it and be cheap (some will point out that prototypes for things like cars can cost millions of dollars while the finished product may cost only $20,000. This doesn't include the cost of tooling or building the factory that mass produces it though. Including that the prototype is a tiny fraction of the cost. ). Some common ones in UX are:
Sketches
Simple paper & pencil sketching is probably the most cost-effective form of prototyping. They're fast and disposable yet help to visualize processes, page flows, graphics concepts, and more.
Mockups
Mockups are primarily used to present and test graphic elements of a UI.
Clickable Prototypes
Clickable prototypes can look like finished UIs or apps. They present screens or pages with at least some elements behaving like the finished product. They might be used to verify usability or features or test interactions.
 Source: What is a Prototype? What are the Roles of Prototypes in Companies?
Source: What is a Prototype? What are the Roles of Prototypes in Companies?
What's NOT a Prototype
Though a prototype may evolve into one, it should not be seen as a final design candidate or MVP. The difference is in the role. Prototypes are intended for testing. That means we need to be willing to throw them out. Also, the UX of the test itself is key in its design. In order to test an element, we may choose to design the rest of the prototype differently that we intend the product. As for the MVP, that is a "VIABLE product". That means it must be intended to be market worthy, to fulfill commercial goals.
Why You Might Want a UX Strategy
Good UX process must include testing the design to get target user feedback on it. The only way to do this effectively is to present the test participants with a presentation of the thing you are testing, a prototype. Prototypes are also a very effective way to present concepts to a team for discussion.
Problems the UX Prototyping Solves
-
Lack of common understanding of a design concept
-
Lack of objective ways of testing the design concepts
-
Lack of management buy-in
How to Implement a UX Prototype
Depending on the phase of the design process and the form of the prototype it may mean drawing on paper, using graphic tools like photoshop, using professional prototyping tools such as Justinmind or Figma.
Resources for the UXPrototyping
Was the article helpful?
Want to write for DXKB?
Feel free to contribute. People from DXKB community will be more than happy.
Related articles
ALL ARTICLES
UX Testing: Goals
UX Testing needs to focus on gaining specific and actionable information that will help the team make better-informed decisions that will, in turn, push the project toward fulfilling the overall UX Strategy. Setting clear goals will help achieve that.
Read moreUX Strategy
UX Strategy gives the design of a user's experience a goal, a plan to reach it, and ways to measure progress and success without which, the project is just a bunch of activities that might lead somewhere but probably not there, where you want it.
Read moreJobs To Be Done
Jobs To Be Done (JTBD) is a theory for understanding the process of consumer life’s transformation. The usage of JTBD improves your product design.
Read moreALL ARTICLES
Contribution
We are happy you want to contribute to DXKB. Please choose your preferred way